Types of PhrasesLanguage is a channel for individuals to exchange ideas. It facilitates and ensures the flow of information. Phrases assist pupils in adding value to content in all sectors of creative endeavor. 
Have you ever wondered why we choose certain words to convey information and how we enable them to make sense? Grammar is the framework of a language, specifically how words are placed together in various means of expressing meaning. Words do not exist alone; in fact they are often combined to create phrases (then clauses and then sentences). A phrase is a combo of words utilised as a unit within a sentence to express or convey a subject. Noun phrases, verb phrases, gerund phrases, infinitive phrases, appositive phrases, participial phrases, prepositional phrases, and absolute phrases are the eight most common forms of phrases. What is a Phrase?A phrase is a set of words that together make what the dictionary refers to as a "conceptual unit" (an idea comprising of a few words). Phrases are typically used as components of clauses. A phrase is not a sentence in and of itself. Because they lack a subject and a predicate, phrases do not make good sense on their own. The phrase's length can range from two to several words. This has nothing to do with whether it is a phrase or a sentence. For instance, "old cat" is a term. "The old, stinky, freezing cat" is another term. So, a phrase is series of words that comprises of no finite verb and functions to complete the sentence to make it valuable and meaningful. Let us explore each of these phrase types in more detail. But, before we do that, and just in case you forgot. A noun is a term used to describe anything, such as an item, location, person, or concept. For example, 'table,' 'city,' 'lady,' and 'love.' An adjective is a term that defines a noun or pronoun. In the line "the dog is black," for example, the adjective "black" is used to define the noun "dog" (the dog). A verb is a word used to describe a certain action or state. In the sentence "the instructor writes on the whiteboard," the verb 'writes' implies the action. The auxiliary verb 'is' specifies the tense of the statement, and the main verb 'rolling' explains the action in the statement "the wheels are rolling down the slope." Adverbsare words utilised for describing the verbs, adjectives, other adverbs, or whole sentences. In the sentence "he walks quickly," for example, the adverb "quickly" includes details about the verb. The adverb 'very' offers information about the adjective in the sentence "he is really huge." A preposition is a word or phrase indicating where something is connected to another. This can apply to relationships in time, space, and direction. Words like 'on,' 'in,' 'under,' 'over,' 'before,' and 'after' are examples. 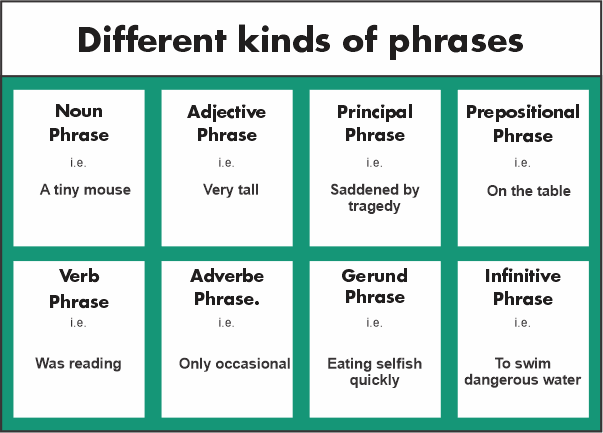
Types of Phrases1. Noun PhrasesA noun phrase is a collection of words that includes a noun (or pronoun, such as he, she, or it) plus other terms that alter the noun. Article (a/an/the), quantifier (some, a lot, a little), demonstrative (this, that, those), possessive (his, her, their), adjective, and adverb can all be modified. Noun phrases are used to provide more details about a noun. They can serve as a sentence's subjects, objects, or complements. In the below mentioned sentence: It is used to provide detail to the phrase by expressing and describing the subject (dog) (a dog that is black in color and belongs to somebody). In the below- mentioned sentence : It is used to denote the sentence's object (a film) and to describe it (terrifying). It has been suggested that a noun phrase can have only one word, which might be a noun or a pronoun. "Helen is heading home from work". Since Helen is the only noun in the statement, this is a one-word noun phrase. So, the noun phrases include a noun?a name, location, or thing?and a minimum of one modifier related to the noun. The modifier may come prior or post the noun. The full phrase will function as a noun in that sentence. Here are a few more examples of the same:
2. Adjective PhraseAn adjective phrase (also referred to as an adjectival phrase) is a string of words that includes an adjective as well as phrases that alter or complement it. Adjective phrases perform the same function or purpose as the adjectives, describing or providing more depth to the nouns or the pronouns. They can appear either prior to or post the noun. Here are a few adjective phrase examples. It comes after the nouns and is often utilized to convey additional information about the noun (the man). In the following sentence : It comes prior to the noun and is utilized to provide additional information about the noun (cookie) - it explains how they tasted (candy-flavored). Here are few more examples of adjectival phrases ;
3. Adverb PhraseAn adverbial phrase (also known to as an adverbial phrase) is a collection of words that includes an adverb as well as other modifiers. They serve as adverbs in sentences and are utilized to alter verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. They might occur either prior to or post the components they alter. In the following sentence : "I go to the fitness centre every Sunday. " It provides extra information about how frequently the action occurs. Here is another example of this type of phrase ; It goes into greater detail on how the action (picked) is performed. Examples of Adverb Phrases instances.
4. Verb PhrasesIn general, every statement will have a verb. However, some actions necessitate a more complex multi-word verb phrase. The phrase is made up of the primary verb/verbs, followed by auxiliary verbs, or aiding verbs. Thus, in this type of phrase, there is a collection of words that includes a head (primary) verb as well as secondary verbs like copular verbs (verbs that connect the subjects to the subject complements, such as sees, looks, and tastes) and auxiliary (helping verbs, i.e., be, do, have). Other modifiers may also be included. A verb phrase serves the same purpose as a verb in a statement. Here are few examples of this type of phrase ; In the following sentence : It is made up of the auxiliary verb 'was,' which denotes the statement's tense, and the primary verb 'strolling,' which denotes the activity. In the following sentence : It is made up of the modal verbs 'will,' which denotes a level of certainty, and the primary word 'go,' which denotes future action. The following are few examples of such verb phrases :
5. Prepositional PhraseA prepositional phrase is a combo of words which includes the prepositions and the objects. Other modifiers may be included, but they are not required. In a statement, a prepositional phrase can function as an adjective or adverb. It is used to alter nouns and verbs and to provide information about subject-verb relationships. Thus, it is a type of phrase that comprises of the prepositions and the objects of the preposition, which is either a noun or a pronoun. Other modifiers characterizing the object of the prepositional phrase may also be included in such a phrase. Consider the following examples: Students are encouraged to show up on time. There are situations when a prepositional phrases will function as adjectives in the sentence. It will be the resply to the inquiry "which one?" As an example,
In the below-mentioned sentence : "The mice run into the box. " The prepositional phrase in the sentence mentioned above is - "Into the box. " It reveals the location of the subject (the mice). Here is another example sentence : It provides information on the location of the subject (the wound). 6. Infinitive PhrasesAn infinitive phrase refers to the one that contains an infinitive as well as a simple verb. There may even be modifiers connected to the phrase's object. It comprises a verb. Therefore, it expresses an action in the statement. In a full sentence, infinitive phrases can function as a noun, adjectives, or adverbs.
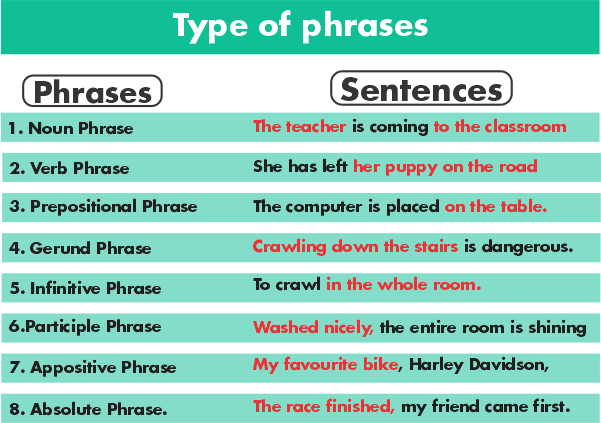
7. Participle PhrasesA participle phrase starts with a participle, which can be either present participles ( concluding with -ing) or past participles (concluding with -ed). The phrases may contain some modifiers and linked terms. Remember that a participle phrase in a statement always appears in the form of an adjective. Here are some instances of participle phrases :
8. Gerund PhrasesA gerund is a term that, with no exception, mostly ends in "-ing." A gerund phrase is one that has an "ing" word, along with certain modifiers in some circumstances. However, participle phrases have a consistent trend (-ing words), so how do you recognize the difference? While participle phrases can be used as adjectives, gerund phrases can only be used as nouns. Consider the following examples :
9. Absolute PhraseAn absolute phrase will include the nouns or the pronouns accompanied by the participle. It could also include more associated terms and modifiers. An absolute participle will alter a whole clause, or perhaps an entire sentence, rather than just one word. It does not, however, comprise a full sentence or clause. Commas are used to separate absolute phrases. Let us look at some instances.
Absolute sentences are the most difficult to recognize. They provide extra details and are usually separated by commas (or dashes). These phrases are unrelated to the remainder of the sentence; they do not specify a particular word but rather affect the entire statement. An absolute phrase comprises of a noun or pronoun as well as several modifiers. The modifier is frequently a participle : The tidal wave coming in, most vacationers were heading home. Here are some additional instances : The course finished, and Kareena sold all her school books. The snow eventually froze over; we went skating. Add an adjective to your nouns or pronouns to create an absolute phrase : Her body covered in sweat; Amanda looked forward to having a bath. Absolute phrase: Her body covered in sweat and hot. Many of these instances could use the word being (her skin being covered in sweat), but you can generally get away without it. You'll also notice how similar these sentences are to clauses. Simply add conjunction and turn the participles into finite verbs : When the snow eventually froze over, we all went skateboarding. Finally, keep in mind that the absolute phrase can appear at the end of the statement 10. Appositive PhraseThe Appositive Phrases refer to the group of words that contain an Appositive and occur post or prior the noun or pronoun that it recognizes or describes. The appositives are the nouns or pronouns that are frequently accompanied by the modifier that sits alongside various other nouns or pronouns to characterize them. Examples of this type of phrase include ;
The appositive in these examples is a noun phrase. However, additional sentences can also be used as appositives: My ambition to play Basketball is what keeps me going. (infinitive phrase ) Matthew's unusual ability, spinning on his neck on the board, provides him with a unique view of life. (participial phrase ) Appositives are excellent for adding additional info to a sentence.
Next Topic#
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










